| ||||
Gram, Acid-fast & Endospore Bacterial Stains - P2
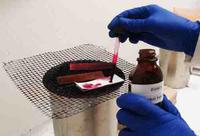
Ziehl’s carbolfuchsin, the primary stain used in acid-fast staining, being applied to a bacterial smear slide covered in blotting paper, over a water bath.
Acid Fast Staining
During the Acid-fast staining technique, a slide-shaped piece of blotting paper is placed over the bacterial smear, a bright pink dye (Ziehl’s carbolfuchsin) is then applied to the blotting paper, and the slide and paper are placed over a water bath (a steaming pot of water covered with a screen) for 3 – 5 minutes.
Page last updated 3/2016
SCIENCE PHOTOS
SPO VIRTUAL CLASSROOMS
PAGE 2 < Back to Page 1
The Virtual Microbiology Classroom provides a wide range of FREE educational resources including PowerPoint Lectures, Study Guides, Review Questions and Practice Test Questions.
What the Acid-fast Stain Reveals about Bacteria
Acid-fast staining, also known as the Ziehl Neelsen stain, is used to identify specialized bacteria that have waxy mycolic acid in their cell wall. The presence of mycolic acid in bacteria is rare, only found in two genera: Mycobacteria
and Nocardia. The bacteria that possess mycolic acid are considered “acid fast,” whereas the vast majority of bacteria, those that do not have cell walls containing mycolic acid, are considered “non-acid fast.”
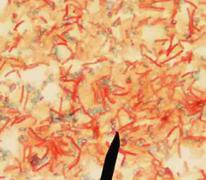
Waxy acid-fast cells stain hot pink and stick together, clumping. Non-waxy (non-acid-fast) stain dark purple. Bacteria viewed at 1000xTM.
After this step is completed, the blotting paper is discarded and the slide is rinsed. A decolorizer, acid alcohol, is then applied to remove the stain from non-acid fast cells. Lastly a purple counter stain (crystal violet) is applied and the slide is rinsed.
After this staining procedure, acid-fast (waxy) bacterial cells are bright pink and non-acid fast (not waxy) bacterial cells are purplish blue.